Risk Management
1. RISK MANAGEMENT PHILOSOPHY AND OBJECTIVES
As a financial services company who carry out the Investment Dealer (excluding underwriting) activities, the Company is naturally exposed in its daily business activities and strategic planning to numerous types of risk, like change in foreign exchange risk rates, undergoing losses due to man-made or natural catastrophes, losing income ability through operational disruptions, outliving of assets and so on. Where there is a risk, there is improbability, and where there is improbability, there is exposure to volatility.
Risk management in practice is where companies steadily identify, quantify and manage the various types of risk inherent to the operations. The most vital goals of a sound risk management program are:
- • To manage the business’s exposure to prospective earnings and capital capriciousness.
- • To capitalize value for the organization’s different stakeholders.
- • Ensuring risk arising from our exposure in the East Africa Market are identified, monitored, quantified and adequately managed.
We are fully committed to maintain our existing strategy of embedding risk management in what we do as it is the source of value creation as well as an essential form of control. It is an integral part of maintaining financial stability for our customers, shareholders and other stakeholders. Our sustainability and financial strength are buttressed by an effective risk management process which helps us identify major risks to which we may be exposed, while instituting appropriate controls and taking mitigating actions for the benefit of our customers and shareholders. The Company risk strategy is to invest its available capital to optimize the balance between return and risk whilst maintaining an appropriate level of economic capital and regulatory capital in accordance with its risk appetite.
Consequently, our risk management objectives are based on the following:
- • Open risk culture: Promote a strong risk management culture amongst our staff, driven by a robust risk governance structure and clear risk appetites. Ensure that sufficient capital surpluses are available to meet the expectations of customers, shareholders and be compliant with regulatory obligations, and whilst meeting our liabilities even if a number of extreme risks were to materialize.
- • Clear accountability: our operations are based on the principle of delegated and clearly defined authority. Individuals are accountable for the risks they take on and their incentives are aligned with the Company’s overall business objectives subject to a rigorous monitoring.
2. RISK MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW
The purpose of this risk assessment is to outline and document the adequacy of the management, operational and technical security and risk mitigation controls that are currently in place to secure the operations of My Investment Markets. This risk assessment provides a structured qualitative assessment of the operational environment. It addresses sensitivity, threats, vulnerabilities, risks and safeguards.
The Company has a defined step by step approach with respect to risk management. The above diagram illustrates the high level process, whereby risks can be managed through the 4 T’s, at each step.
Treat: Take action to control the risk either by reducing the likelihood of the risk developing or limiting the impact it will have on the project
Transfer: Some of the financial risks maybe transferable via Insurance or accepted by third parties (liquidity provider)
Tolerate: Nothing can be done at a reasonable cost to mitigate the risk or the likelihood and impact are at reasonable level
Terminate: Do things differently and remove the risk
2.1 SCOPE
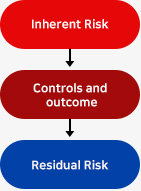
2.1.1 TYPES OF RISKS – INHERENT V/S RESIDUAL
The inherent risk is the one that exists before a company addresses it, that is the risk to the Company in the absence of any action taken to alter either its likelihood or its impact. Every company faces it, not all manage it effectively. These risks are reflected mainly on how you do business; its complexity, growth, changes; the staffing; technology and the organizational structure. The residual risk is also known as “vulnerability” or “exposure”.
It is the risk that remains after the company has attempted to mitigate the inherent risk. Adopting the approach of Enterprise Risk Management within the Company, where management provides assurance and internal audit provides reassurance, management is responsible for:
- • Assessing the inherent risk (i.e., before mitigation and controls).
- • Assessing the effectiveness of existing risk mitigation and controls.
- • Determining the residual risk (i.e., the risk that remains after mitigation and controls are implemented).
- • Determining whether such exposure is within the company’s risk appetite for that type of risk, and if not, taking additional steps to mitigate the risk.
- • Providing reasonable assurance to the board that the controls are both effective and efficient in managing the exposure so that it remains within the board-approved appetite for that type of risk.
The diagram below illustrates how the Company’s risk control framework minimizes the number of inherent risks to residual ones. The duty of the risk management is to review continuously the internal controls of the inherent risks and to monitor closely the residuals risks while taking actions when appropriate.
| Inherent Risk | Control/Mitigation | Outcome | Residual Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Disaster | Management Plan | Move office, resumes | Phase resumption of operations |
| Cyber attack (Virus, Hacker) | Cyber Security Framework | can avoid of loss data | Contained cyber Risk |
| Onboarding High risk clinet | conduct enhance due diligence | Strong client base | Client might not accepted due to high risk |
| Non Compliance to regulation | Compliance framework | Compliance with applicable laws and regulation | which may cause misunderstanding |
| Lack of well-trained staff | Training policy | Knowledgable staff | Staff might exit the company due to turnover |
2.1.2 Risk Management Responsibilities
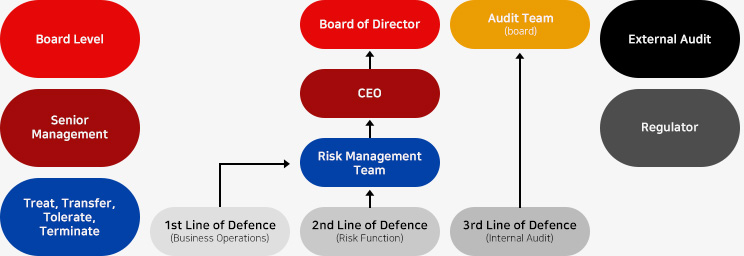
The Company has adopted the ‘three-lines-of-defence’ model where ownership for risk is taken at all levels in the Company. This model is widely adopted by financial services companies globally. It clearly sets out the risk management responsibilities across the business and is consistent with the current regulatory risk-based approach, encompassing corporate governance, systems and controls.
| CEO | Board | |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy, Risk Appetite and Policy | ||
| 1st line | 2nd line | 3nd line |
| Doing and recording | Internal verification | Independent Verification |
| management based | Risk and legal based | Independent based |
|
Delegate authority to: 1. Develop and implement internal control within the key process of operational clusters according to risk apetite statement 2. Manage risk 3. Escalate new risk |
Objective oversight of risks. Key activities include: 1. design and deploys the overall risk management and compliance frameworks 2. Develops and monitors policies and procedures 3. monitor adherence to framework and strategy |
Independent and objective assurance over the effectiveness
of corporate standards and business complaince 1. Independent assurance that the risk management process is functioning as designed and identifies improvement opportunities |
2.1.3 Risk Management Framework
The Group Audit and Risk Methodology is fully riskbased and aligned on COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission) Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework. The COSO ERM Framework is the broadly accepted standard against which organizations can benchmark their internal control activities. The Mauritius Union Group’s risk management framework forms an integral part of the management and Board processes as well as the decision-making framework across the organisation. The key elements of the risk management framework are illustrated below:
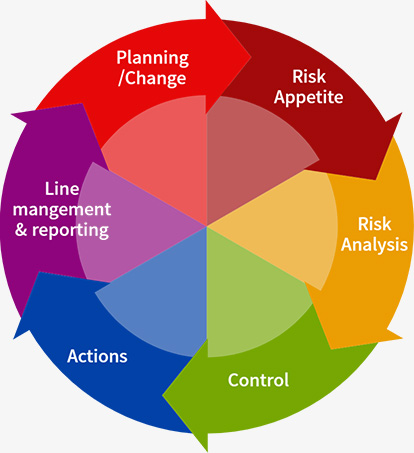
| Insight | Oversight |
|---|---|
| Management | Governance |
| Incident & loss Events (learn from past) | Roles and delegated authorities |
| Risk Profiles & Quantification Analysis (Present) | Policies |
| Predict events (Future) | Committies |
| Systems and Tools Communications, Education, Training and Guidance | |
2.1.4 Risk Appetite
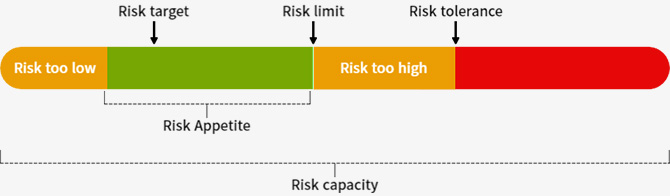
The risk appetite is the level of risk the Company acknowledges and is able to accept in the pursuit of its strategic objectives. The strategic and operational planning process supports the group in optimally exploiting its opportunities. This involves the consideration of the portfolio of opportunities identified by businesses, leading to decisions by the Board in relation to the opportunities the Company wishes to pursue. Capital is allocated to businesses to support delivery of these plans. The Company’s required returns will be reflected in the targets set for businesses, including targets for return on capital employed, growth in business and profitability and dividend payment expectations. The Company’s business plan, capital allocation and business targets are therefore a key component of the group’s risk appetite. Risk appetite will accordingly continually evolve and be reviewed.
2.1.5 POLICIES AND PROCEDURES
To inculcate a consistent and rigorous approach to risk management across all the businesses in which we operate, we observe a set of formal risk policies. These delineate risk management and control requirements for the Company’s operations. As our business responds to changing market conditions and customer needs, we regularly monitor the appropriateness of our risk policies to ensure that they remain up-to-date.
We regularly identify and review risk exposures. Where risks are outside of tolerance, action plans are required. Similarly, controls are regularly reviewed for effectiveness and corrective actions implemented where necessary. This helps to provide assurance to the various risk oversight committees that there are appropriate controls in place for all our core business activities, and that the processes for managing risk are understood and followed consistently across our businesses.
2.1.6 THE RISK PROFILE
| RISK MANAGEMENT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| External Development | Strategic | Customer profile | Operational | Financial |
| Strategy & planning | Customer profile | Regulation | Capital management | |
| IT & Business protection | Fiancial reporting | |||
| Financial crime | ||||
| Business continuity planning | Customer mangement | People | Reserving | |
| cost of terminal and liquidity provider Mangement | ||||
| Health and safety | Liquidity | |||
| CRITICAL RISK | MANAGEMENT AND MITIGATION EXAMPLES |
|---|---|
| Strategic risk | |
| Definition: The risk of a negative impact on the company’s value, arising from the adverse effect of management decisions regarding business strategies and their implementation. This risk reflects on the compatibility between strategic goals, business continuity management and the resources deployed to achieve those goals. Strategic risk also includes the lack of management’s ability to effectively analyse and react to external factors (e.g. market conditions/ natural catastrophes) which could affect critical operations of the Company and prevent critical services to be resilient. Owner: Chief Executive Officer | |
| Strategy & Planning |
|
| Business Continuity Management |
|
| Customer, Products & Markets Risk | |
| Definition: Our operation, there may be a risk related to customer management trading, deposit, withdrawal, company brandname, products and distribution management which can cause significant damage to the Company’s reputation, profitability, future business. | |
| Customer |
|
| Distribution Management |
|
| Brand & Marketing Communication |
|
| Environment |
|
| Operational Risk | |
|
Definition: operational risk refers to the risk of loss
resulting from the failure or inadequacy of internal
processes, people, and systems used in the process of
brokering transactions between buyers and sellers of
financial instruments. Operational risks for Company may include errors in trade processing, technological failures, fraud or misconduct by employees or clients, regulatory non-compliance, and other risks associated with the day-to-day operations of the brokerage business. Effective management of operational risk in the Company involves identifying and assessing these risks, implementing effective risk management procedures and controls, monitoring and reporting on risk exposure, and continually improving the risk management framework to ensure ongoing effectiveness. This is essential to protect the firm's reputation, maintain client trust, and ensure the long-term viability of the business. |
|
| Information Technology | Improved performance of our IT systems across the board, while focussing on the development of future system capability is key for us. With significant changes might be taken once we expanding, we will always monitor risks associated with out IT systems’ stability, cyber security and internal control environment. |
| Legal & Regulatory | We work towards efficient and customer friendly processes while having a strong risk based approach to minimise exposure and ensure robustness of processes. |
| Financial Crime |
|
| People |
|
| Outsourcing |
|
| Health & Safety |
|
| Communications |
|
| Financial Risk | |
| Definition: Financial Risks as the term suggests is the risk that involves financial loss to firms. It generally arises due to instability and losses in the financial market caused by movements in stock prices, currencies, reserves, interest rates and more. Our focus is on capital management which is an accounting strategy that strives to maintain sufficient and equal levels of working capital, current assets, and current liabilities at all times. | |
| Capital Management |
|
| Financial Reporting |
|
| Reserving |
|
| Liquidity |
|
Periodic Reviews
Depending on the level of risk, the Company’ systems will set up a schedule to: review the customer file to see if it needs adjusting/updating; carry out another screening on the customer; check if the business relationship remains within the risk appetite of the Company; and ensure a STR in relation to a customer does not need to be filed with the Authorities. The Company’s periodic review schedule is listed below:
| Customer Rating | Refresh | Customer Documents / Re-screen |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Every | 2years |
| Medium | Every | 1years |
| High | Every | half year |
5. BUSINESS POLICY TESTING
During the risk assessment of Investment Markets all related policies were inspected and tested against local regulations and international best practice. All policies were found to be adequate in addressing the full spectrum of risks associated to the business and drafted in accordance with applicable legislatures.
These policies include:
- • Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing Policy / KYC Policy
- • Internal Control Policy
- • Disaster Recovery Plan
- • Complaint Handling Policy
- • Privacy Policy (with having EU GDPR as a milestone)
- • Risk Disclosure Policy
- • Risk Management Policy
6. SERVICE/PRODUCT RISK ASSESSMENT
Investment Markets recognises the risks of it being used for money laundering or terrorist financing derive from the products and services that it offers. The purpose of the Product Risk Assessment is to assess the level of Money Laundering or Terrorist Financing Risk posed by the product or service offerings of the business and then to document the mitigation elements thereof.
In accordance with the Companies AML/CFT Programme Policy, the Company adopts a risk based approach to managing its money laundering and terrorist financing risks. Such an approach is essential to the effective allocation of resource to areas of highest risk and to the implementation of systems and controls that are proportionate to the risks and appropriate to the nature, scale and complexity of the operations.
Investment Markets ‘s business is based exclusively on the provision of CFD transactions with customers. Hence the product risk remains constant for all customers and the business and is built into the Customer Risk Assessment methodology of the Company. The product/service itself is considered to pose a low risk of money laundering for the following reasons:
- • the limited ability to receive and make payments to third parties;
- • the traceable nature of transactions;
- • the potential volatility in value of the product/service;
- • the lack of anonymity of the product/service;
- • the product/service cannot be purchased with cash.
In its 2009 report titled “Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing in the securities sector” the FATF outlined the following vulnerabilities associated with CFD market access:
- 1. The number of firms offering the service has increased and can have substantial transaction volumes. These high transaction volumes can create a “Black Box” and increases the difficulty for financial institutions to understand transactions occurring in the account.
- 2. Non-face-to-face onboarding increases the risk of a firm not adequately identifying its customers.
Both points 1 and 2 have been mitigated by the Company by ensuring that adequate transactional monitoring software is employed and that all customers are adequately screened and vetted before they are accepted as clients of the Company
After taking account of all these factors and industry experience, the product/service risk is assigned a overall risk rating of Low and any risk emanating from this segment has been adequately mitigated by the Company.
7. GEOGRAPHICAL RISK ASSESSMENT
Investment Markets recognises the risks of it being used for money laundering or terrorist financing derive primarily from the jurisdictions in which it operates. The Company has developed its own AML Country Risk Matrix approach which ranks the money laundering risk of a particular country according to where it appears on a number of indices, including UN sanctions lists, FATF Country Risk and more.
The purpose of the AML Country Risk Matrix is to assess the level of Money Laundering or Terrorist Financing Risk posed by a particular country and allows the business to set strict parameters for which countries it accepts. The AML Country Risk Matrix groups countries into the following categories, with associated rules applied:
| Status | Rule | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Blacklisted | May not accept clients from these countries (override customer risk rating) | Sudan |
| High Risk | Apply Enhanced Due Diligence for clients from these countries | Ghana |
| Medium Risk | Apply Standard Due Diligence for clients from these countries (Only IF overall customer risk rating is also Medium) | Angola |
| Low Risk | Apply Simplified Due Diligence for clients from these countries (Only IF overall customer risk rating is also Low) | UK |
The country of residence and the nationality of a prospective customer plays a significant part in a customers overall AML risk rating. Customers from Blacklisted countries will be prevented from opening and or operating accounts with the Company.
After taking account of all these factors and industry experience, the country risk is assigned a overall risk rating of Moderate but is more than adequately mitigated by the employment of the Companies AML Country Risk Matrix.